Micro CT and Micro MRI imaging of a mouse skull, showing hard and soft tissue….Continue Reading Dynamic imaging
Dynamic imaging
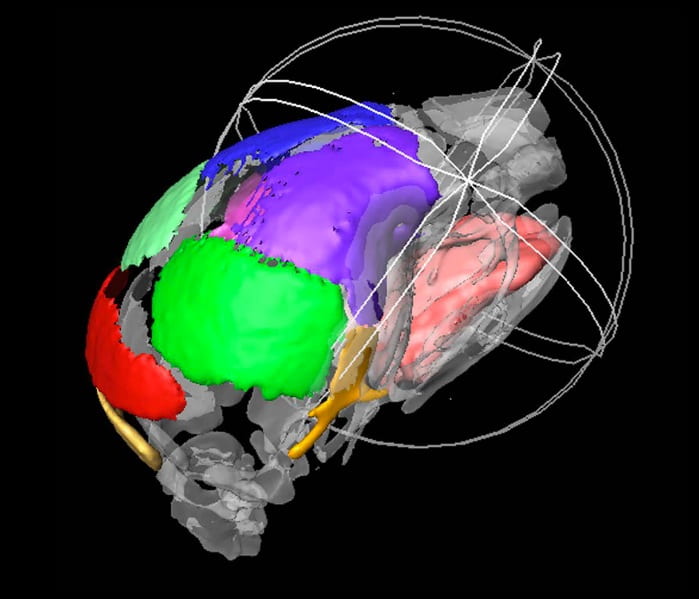

Micro CT and Micro MRI imaging of a mouse skull, showing hard and soft tissue….Continue Reading Dynamic imaging
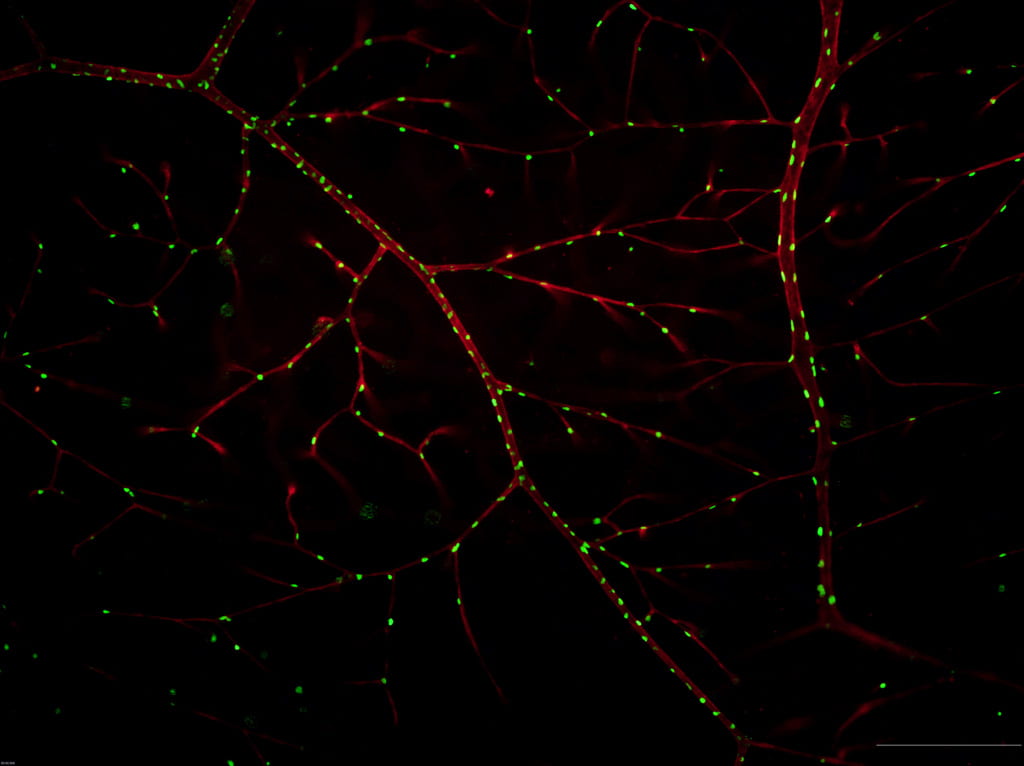
Stem cells located near vasculature in the retina. Red: GS-IB4 staining, labeling the endothelium. Green: H2BGFP labeling nuclei derived from neural crest cells. Image from Yang Chai’s lab….Continue Reading Stem cell research
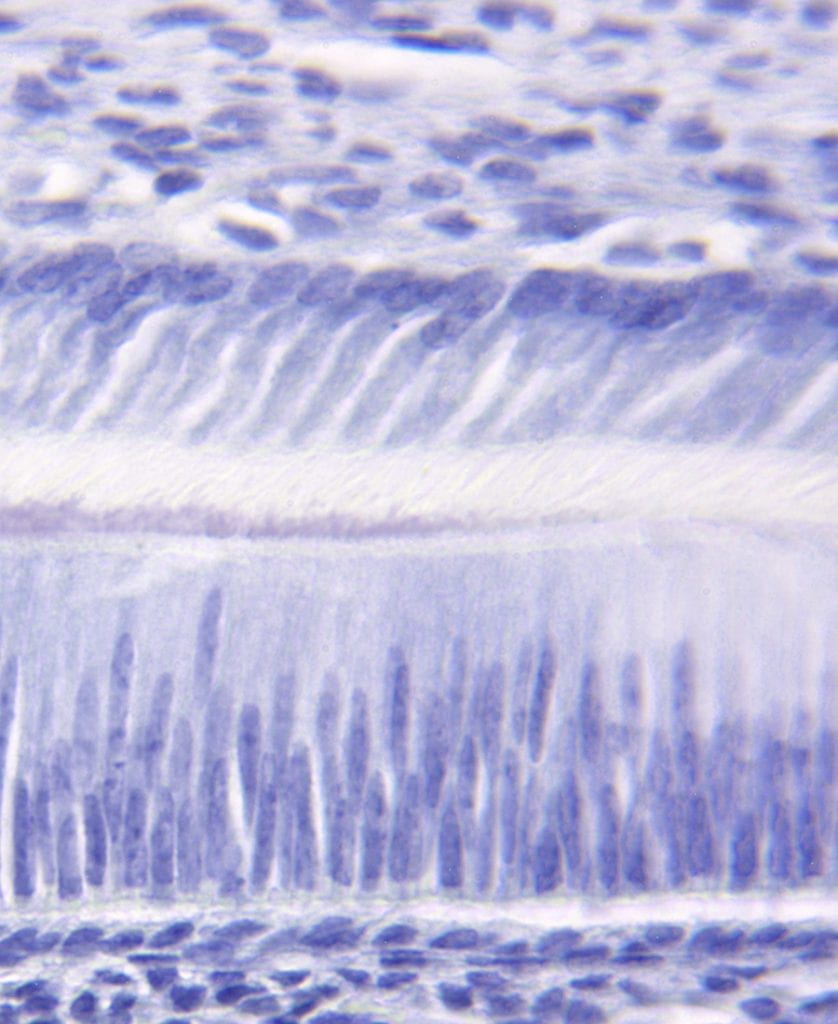
Polarized odontoblasts (top) and polarized ameloblasts (bottom) forming the initial dentin and enamel during tooth formation. Image from Michael Paine’s lab….Continue Reading Understanding tooth formation
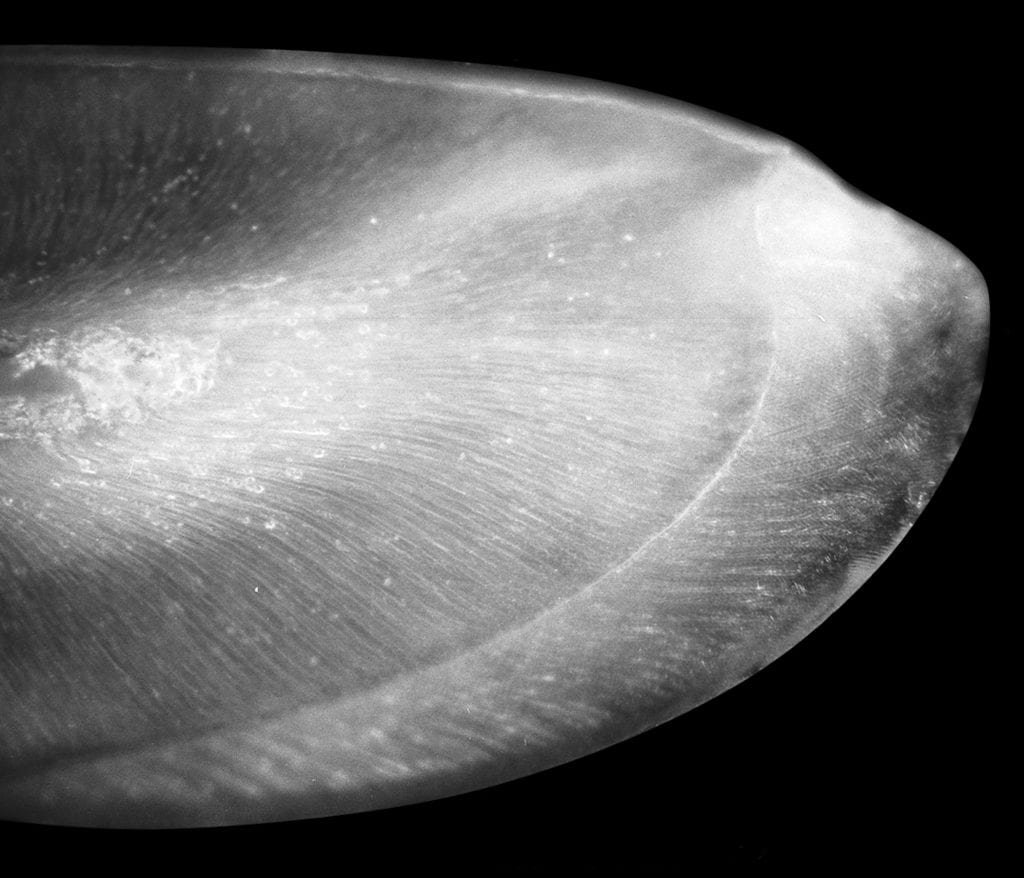

Polished coronal section from a mandibular incisor tooth of a 6-week old transgenic mouse over-expressing dentin sialoprotein in the enamel matrix. The mesial aspect of the tooth is to the top, and the labial aspect is to the right. The junction between the enamel and the underlying dentin (dentino-enamel junction) is clearly evident. Image from…Continue Reading Tooth enamel research
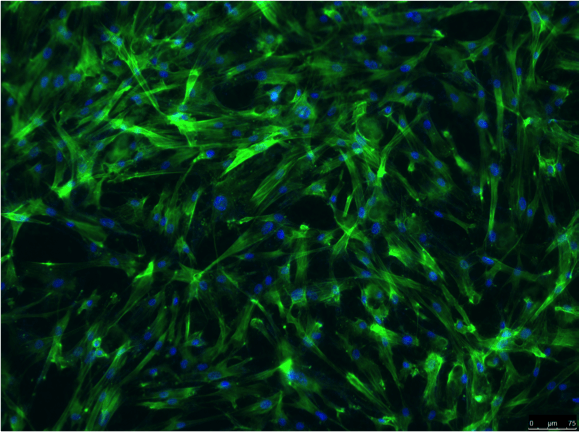
Fluorescence microscopy image of periodontal ligament stem cells cultured (14 days) on titanium surfaces coated with amelogenin-apatite nano-composite. Image taken by JinPu Chu, Visiting Scholar in Oldak’s group….Continue Reading Biomaterials research

Confocal images of mouse mandibular molars showing immunofluorescence of amelogenin (green) and enamelin (red) at postnatal day 3. Co-localization of amelogenin and enamelin is revealed by overlapping signals resulting in yellow/orange staining. Nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue). Image taken by Postdoctoral Associate Victoria Gallon. Scale is 100 microns….Continue Reading Understanding enamel formation
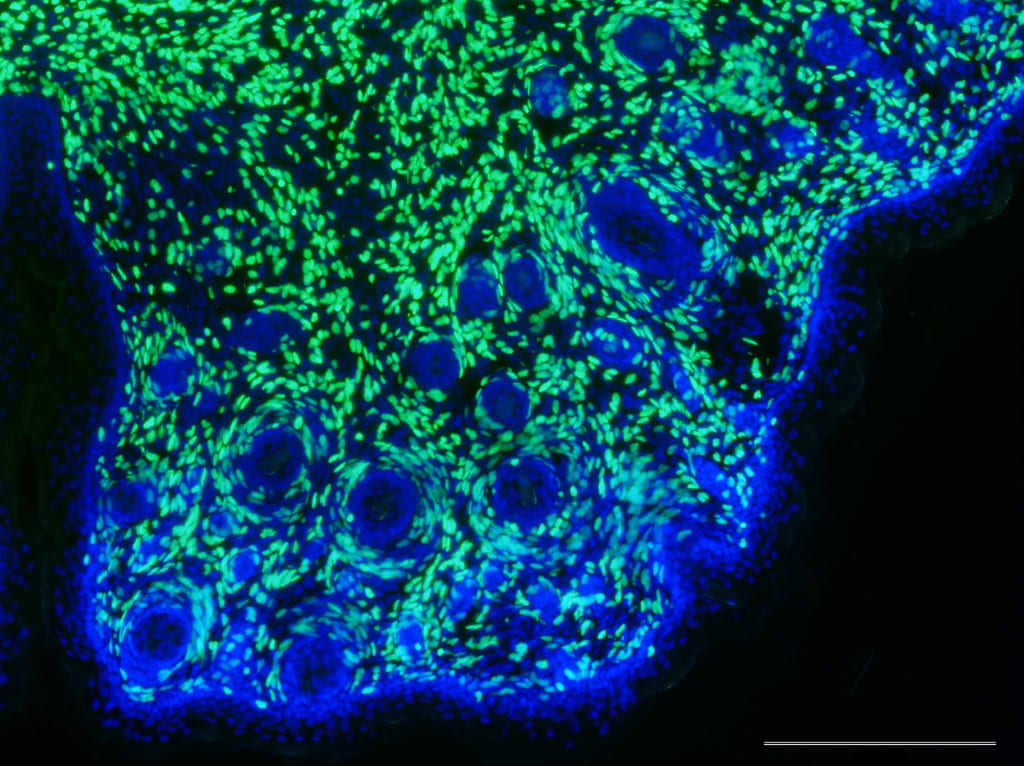
Whisker pad tissue section. Green: H2BGFP labeling nuclei derived from neural crest cells. Blue: DAPI staining, labeling nuclei of all tissues. Image from Yang Chai’s lab….Continue Reading Stem cell research
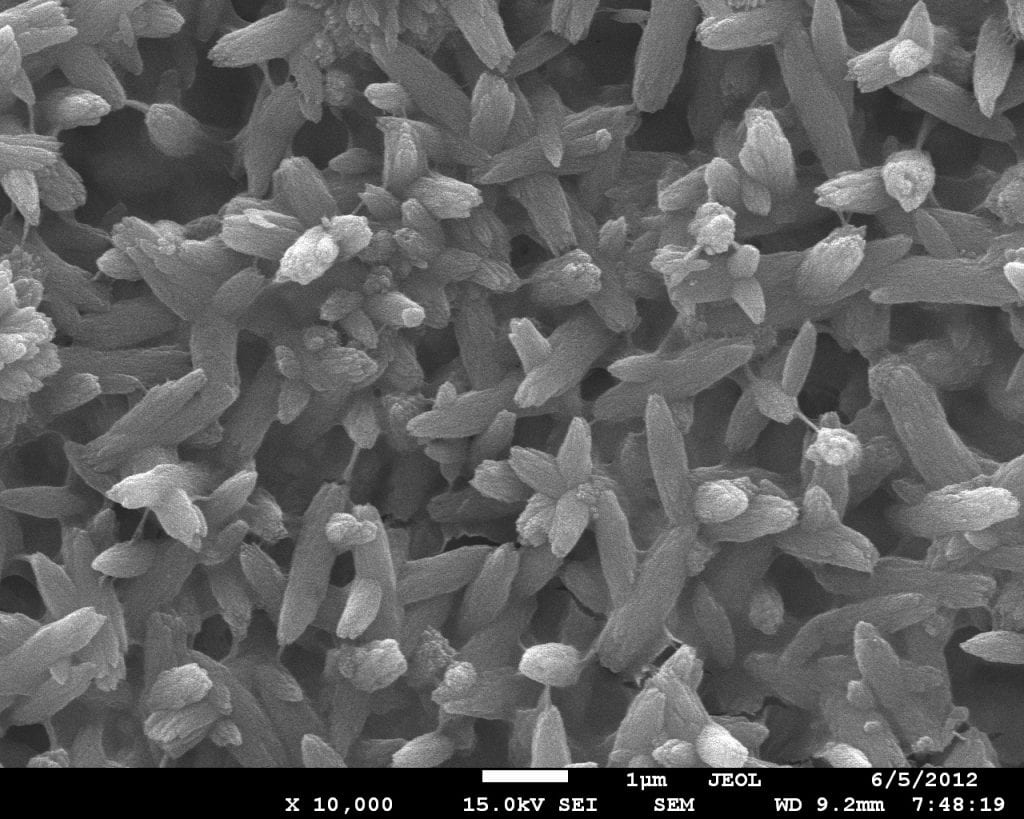

SEM image shows the morphology of a newly-grown apatite layer formed in chitosan hydrogel without amelogenin after remineralization in an artificial saliva solution for 7 days. Image from Janet Oldak’s lab….Continue Reading Biomaterials science
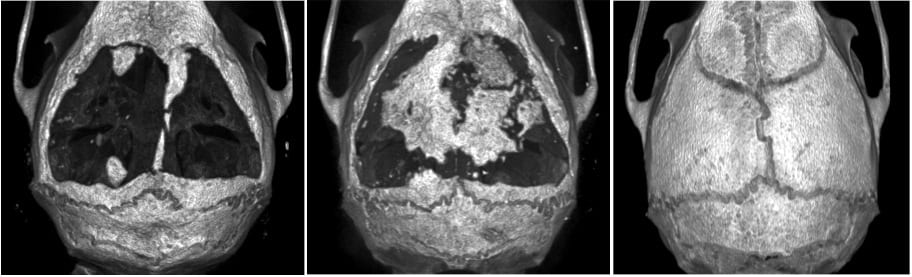
Immune cells govern cell-based tissue regeneration: MicroCT images showed that mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) failed to repair over-sized calvarial defects (center; no treatment, left). However, infusion of regulatory T cells (Treg) significantly improved MSC-based calvarial regeneration (right)….Continue Reading Tissue regeneration
Adaptor protein complex 2–mediated, clathrin-dependent endocytosis, and related gene activities, are a prominent feature during maturation stage amelogenesis. Lacruz RS, Brookes SJ, Wen X, Jimenez JM, Vikman S, Hu P, White SN, Lyngstadaas SP, Okamoto CT, Smith CE, Paine ML. (2013) Journal of Bone and Mineral Research 28(3): 672-87….Continue Reading New Article: Adaptor protein complex 2–mediated, clathrin-dependent endocytosis, and related gene activities, are a prominent feature during maturation stage amelogenesis